Ever puzzled over the sudden appearance of skin rashes and how they disrupt your life? Grasping the various causes of skin rashes is key to identifying, treating, and preventing them effectively.
This detailed guide explores 22 distinct skin rashes, covering their causes, visual signs, and treatment methods. From eczema and psoriasis to shingles and rosacea, each condition presents unique symptoms and triggers. Accurate identification and expert medical advice are vital for managing these conditions. Learn about each rash type, how to identify them through pictures, and the most effective treatment options.
Whether it’s a sudden outbreak of itchy bumps or chronic skin inflammation, our guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and solutions you need. Skin rashes can affect anyone, anywhere. Understanding and managing them can protect your well-being from future outbreaks.
Key Takeaways
- Skin rashes can result from various causes such as infections, allergens, or autoimmune disorders.
- Identifying specific rashes through visual characteristics and pictures is critical for accurate treatment.
- Common rashes like eczema, psoriasis, and shingles have unique symptoms and require individualized care.
- Consulting healthcare professionals for diagnosis ensures personalized treatment and management.
- Preventive measures and lifestyle modifications play a significant role in minimizing rash occurrences.
Understanding Skin Rashes: An Overview
In this section, I’ll shed light on the complexities of skin rashes. We’ll explore their origins, common types, and symptoms that should prompt you to seek professional advice. Recognizing the wide array of possible causes and manifestations is key for effective treatment and management.
What is a Skin Rash?
A skin rash is typically an area of irritated or inflamed skin. It can present as red, bumpy, or scaly patches. These types of skin rashes can appear in various forms, from mild to severe, and can occur in any part of the body. Often, skin irritation is the first noticeable sign, prompting discomfort and the need for medical evaluation to determine the underlying causes of skin rash.
Common Causes of Skin Rashes
There are myriad causes of skin rash, ranging from allergic reactions to infections. Contact dermatitis, for instance, is frequently reported due to exposure to irritants or allergens, accounting for a significant percentage of dermatology visits4. Bug bites, such as those from ticks, can lead to Lyme Disease, affecting approximately 300,000 people annually in the United States4. Other rashes, such as those caused by viral infections, are prevalent in pediatric populations5. Understanding these causes is vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms to Watch For
The symptoms of skin rash are diverse, including redness, itching, and swelling. For example, diaper rash affects up to 35% of infants at some point, typically presenting with redness and discomfort in the diaper area4. Other rashes, such as atopic dermatitis, affect approximately 10-20% of children globally, leading to chronic, itchy skin conditions4. Recognizing these symptoms early on can lead to timely and effective interventions, mitigating long-term impacts.
Flea Bites: Identification and Treatment
Flea bites are known for their small, itchy red bumps. They often appear in clusters or lines on the lower legs and feet. Recognizing these bites involves noting their distinctive pattern and symptoms. These symptoms become more pronounced at night, due to the increased irritation activity of these insects.
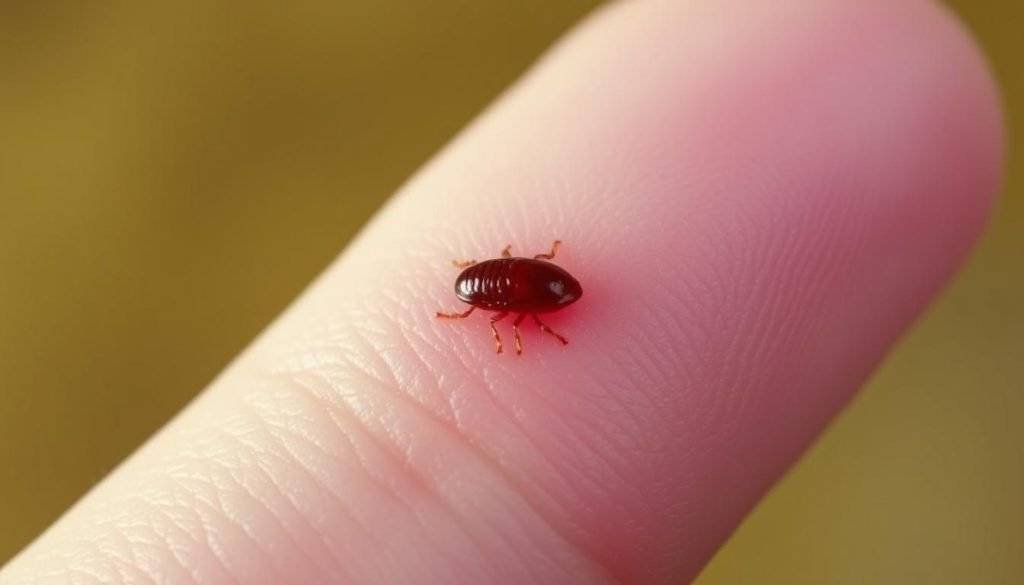

Appearance and Symptoms
Flea bites can appear as small, discolored bumps with a central red spot on lighter skin tones. On darker skin tones, they may blend with the surrounding skin or appear darker6. These bites are commonly found around the feet and ankles but can occur on any exposed skin, including arms and scalp6. The “breakfast, lunch, and dinner” sign – three or more bites in a linear or triangular pattern – is a key indicator of flea bites7.
Flea bite symptoms can lead to further complications like infections and allergic reactions. These may manifest as swelling, redness, and in rare cases, even anaphylaxis6. Children are at a higher risk of parasite infections from flea bites, as they spend more time on the floor where fleas are likely to hide8.
Steps for Effective Treatment
Treating flea bites promptly involves several key steps. Start by thoroughly cleaning the affected area with soap and water to minimize the risk of infection. Applying topical antihistamines or corticosteroids can help reduce itching and inflammation, providing relief from the irritating symptoms of flea bites7.
For flea rash treatment, an ice pack or a cool cloth can be applied to the swollen areas to soothe the skin. If there are signs of a more severe reaction, such as significant swelling or difficulty breathing, seek medical advice immediately. Remember, using measures like laundering bedding at high temperatures, regular vacuuming, and utilizing flea foggers can help eliminate fleas from your living environment, preventing future bites6.
Should symptoms like swollen glands, fever, chills, headache, or muscle aches occur, consult a healthcare provider. This is to rule out any serious infections or complications stemming from flea bites6. This approach ensures both immediate relief and long-term protection against these pesky invaders.
Fifth Disease: Viral Rash in Children
Fifth disease is a common viral infection among children, characterized by a distinctive rash and other flu-like symptoms. This infection typically affects children aged 5 to 15 years and is caused by parvovirus B199. Let’s explore the symptoms, treatment options, and prevention tips for managing this condition.
Recognizing Fifth Disease
Identifying fifth disease involves recognizing several key symptoms. Initially, children may experience a low fever, headache, and nasal congestion9. The hallmark sign is the notorious “slapped cheek” rash, which appears as a bright red rash on the face and can spread to the trunk and limbs within a few days. This raised rash typically shows up 4 to 14 days after infection and can last between 1 to 3 weeks10. In some instances, children younger than 10 years are more likely to develop this characteristic rash9. Approximately 10% of children may also experience joint pain and swelling10.
Treatment Options
When it comes to treating Fifth disease, the primary focus is on symptom relief, as there is no cure or vaccine available for this viral infection9. Parents can provide fever reducers like acetaminophen, ensure their child remains adequately hydrated, and allow plenty of rest. In some cases, parvovirus B19 can lead to severe anemia requiring hospitalization for treatment, though this is rare9. For those experiencing joint pain, over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications may be beneficial. Interestingly, once a child recovers from Fifth disease, they gain lifelong immunity and are unlikely to contract the infection again9.
Prevention Tips
Preventing Fifth disease hinges on practicing good hygiene and minimizing exposure to infected individuals. Here are some effective prevention measures:
- Wash hands regularly: Frequent and thorough hand washing is the most effective way to prevent the spread of the virus9.
- Avoid close contact: It’s important to avoid close contact with those showing early flu-like symptoms, as the virus is most contagious before the rash appears9.
- Sanitize surfaces: Clean commonly touched surfaces to reduce the virus’s presence in shared environments.
- Educate children: Teach children the importance of hygiene to protect themselves and others from viral rashes in children.
About 20% of children infected with parvovirus B19 do not exhibit flu-like symptoms but can transmit the virus10. Maintaining consistent hygiene practices within schools and households is key to preventing Fifth disease. Remember, while complications from this viral infection are rare, the steps we take can significantly lessen the spread and impact of Fifth disease.
Rosacea: Managing This Chronic Rash
Understanding rosacea is key to managing it. It’s important to know what triggers it and explore treatment options. By being proactive, you can improve your quality of life and keep your skin healthy.
Common Triggers
Rosacea triggers vary from person to person. Hot drinks, spicy foods, weather extremes, and emotional stress are common ones. Alcohol and sun exposure can also worsen symptoms like facial redness and swelling1112.

Avoiding these triggers is essential for effective rosacea management.
Effective Treatments
Treating rosacea requires a variety of approaches. Topical treatments like brimonidine (Mirvaso) and oxymetazoline (Rhofade) can quickly reduce facial redness, with effects visible within 12 hours11. Azelaic acid and metronidazole are also used, though results may take 2 to 6 weeks to show11. For severe cases, oral antibiotics such as doxycycline (Oracea) or isotretinoin are prescribed11.
Laser therapy is another option for improving blood vessels and chronic redness, providing more substantial results than topical treatments11. Tailoring treatment plans to individual needs is important for optimal results.
Creating a skincare routine sensitive to rosacea is critical. Choose fragrance-free products and avoid irritants like alcohol and menthol11. Daily gentle facial massages and stress management techniques like deep breathing can also help11. Using mineral-based sunscreens with at least SPF 30 is recommended to prevent sun-triggered flare-ups11.
- Brimonidine and oxymetazoline: Effective within 12 hours11.
- Azelaic acid and metronidazole: Results in 2-6 weeks11.
- Ivermectin: Longer than 6 weeks but lasts longer11.
- Laser treatment: Often more effective for blood vessels and redness11.
- Minimize triggers: Focus on lifestyle adjustments1112.
By understanding and managing rosacea, you can take control of your skin health. This empowers those with this chronic skin rash to improve their comfort and appearance significantly.
Impetigo: A Contagious Bacterial Infection
Impetigo is a highly contagious skin infection that mainly affects infants and children, aged 2 to 5 years. It is caused by streptococcus or staphylococcus bacteria, leading to red sores or blisters that burst, forming crusty, golden-brown patches. These sores typically appear around the nose, mouth, and hands. The infection spreads rapidly through direct contact with sores or contaminated items like clothing and towels. It’s essential to understand the symptoms and treatment options1314.
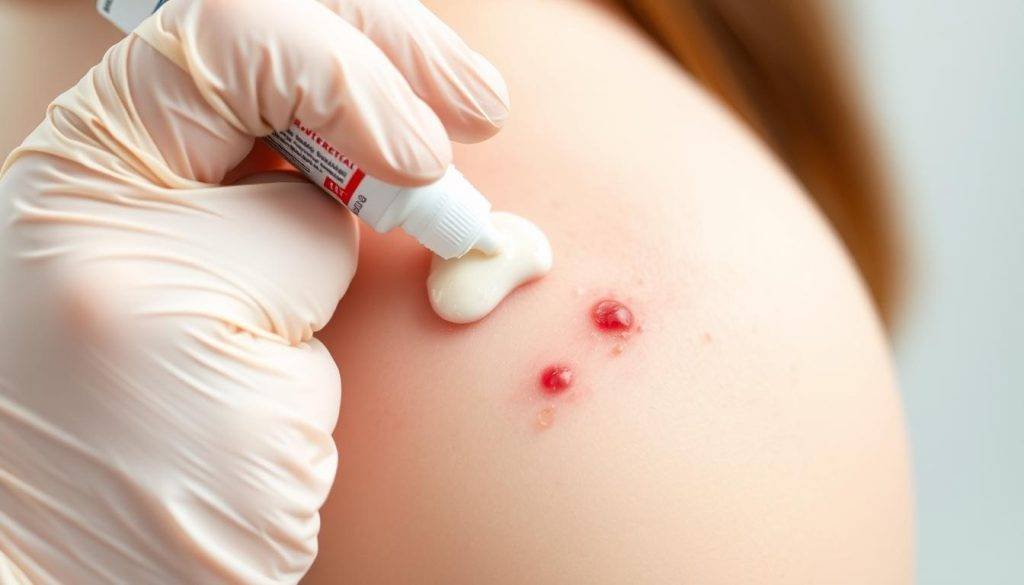
Symptoms and Causes
- Red sores or blisters that burst and leave crusty, golden-brown patches around the nose, mouth, and hands.
- Symptoms of impetigo can develop within three days after the bacteria infect the skin15.
- Staphylococcus aureus causes 80% of non-bullous impetigo cases, while Group A streptococcus is responsible for 10%15.
- Individuals with pre-existing skin conditions or damaged skin are at a higher risk of developing this bacterial skin rash13.
- In warm, humid weather conditions, impetigo infections are more prevalent14.
How to Treat Impetigo
Effective impetigo treatment involves maintaining good hygiene and the use of antibiotic creams or tablets. Here are the steps for treating this bacterial skin rash:
- Clean the affected area gently with soap and water to remove crusts and bacteria.
- Apply topical antibiotic ointments, such as mupirocin or hydrogen peroxide cream, three times a day for 5 to 7 days1315. For more severe cases, your doctor may prescribe oral antibiotics.
- Keep sores covered with gauze or bandages to prevent the spread of the infection14.
- Monitor for signs of improvement within 48 hours. If symptoms of impetigo persist, consult a healthcare provider for reassessment13.
- Preventing the spread of impetigo involves practicing good hygiene, such as regular handwashing and avoiding sharing personal items1314.
By understanding the symptoms of impetigo and implementing effective impetigo treatment, we can significantly reduce its impact. Awareness and early intervention are key to managing and preventing further bacterial skin rash outbreaks in our communities.
Ringworm: Fungal Infection of the Skin
Ringworm, also known as tinea, is a prevalent fungal skin infection impacting various body areas. Early recognition of symptoms is key for effective treatment and containment of the infection.
Identifying Ringworm
Accurate ringworm identification is essential for prompt treatment. The infection manifests as a red, circular, and scaly rash with a clearer center. Typically found on the buttocks, trunk, arms, and legs, it can spread through direct contact or shared items like towels and clothing16.
Treatment and Medication
Effective ringworm treatment often involves over-the-counter antifungal creams, gels, or powders. Common OTC options include Clotrimazole, Miconazole, Terbinafine, and Tolnaftate17. If symptoms persist or worsen, prescription oral antifungal medications may be required, typically for one to three months16. Antifungal shampoos like ketoconazole can help manage scalp ringworm but do not cure it17. Exploring natural remedies may also offer relief.
Preventing Ringworm Spread
Preventing ringworm is critical due to its contagious nature. Good hygiene, avoiding shared items, and keeping skin clean and dry are effective preventive measures. The fungus can survive on surfaces for months, making disinfectant sprays or bleach essential for thorough cleaning17. Implementing these strategies can significantly reduce the spread of fungal infections.
Contact Dermatitis: Allergic Reactions and Irritations
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin reacts negatively to allergens or irritants, causing red, itchy, and inflamed areas. This condition can affect various parts of the body, with hands and face being the most commonly impacted areas18. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment methods is key for effective management and prevention.
Causes of Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is categorized into two types: irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis. Irritant contact dermatitis is often triggered by substances like soaps, detergents, and solvents18. On the other hand, allergic contact dermatitis results from an allergic reaction to specific substances, such as nickel in jewelry, fragrances in perfumes, and certain plants like poison ivy19. Women are more prone to this condition due to nickel allergies from jewelry20. Healthcare workers, cleaners, and florists are at higher risk due to frequent exposure to allergens20.
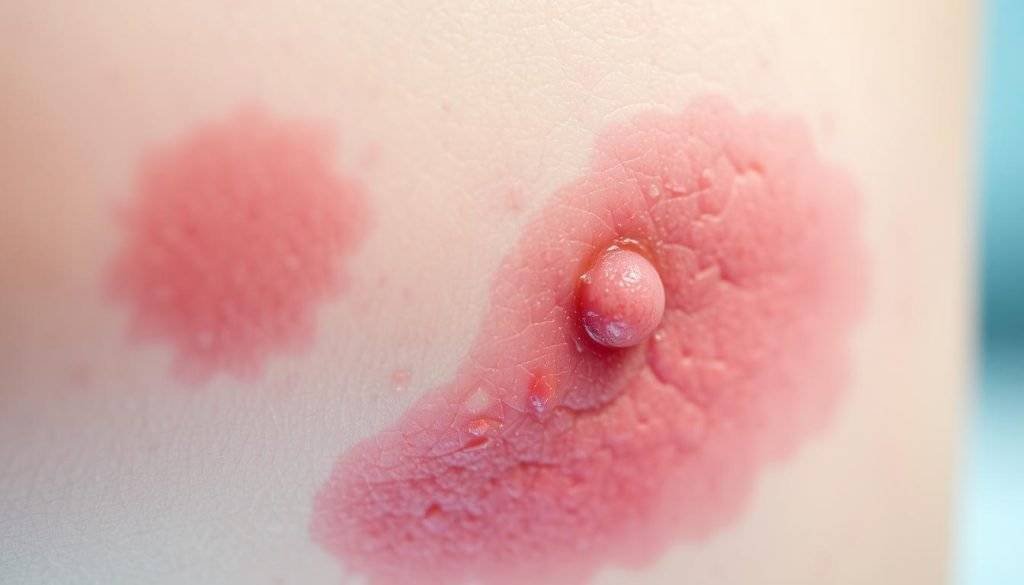
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of contact dermatitis generally appear 48-72 hours after exposure to the allergen or irritant20. They can manifest as redness, itching, swelling, blistering, or dryness of the skin20. Diagnosing involves patch testing to identify specific allergens, essential for severe or recurrent cases20. Proper diagnosis is vital for informing the treatment plan and preventing future occurrences.
Treatment Options
Treating skin allergies from contact dermatitis involves avoiding known allergens and irritants. Management strategies include using emollient creams to keep the skin hydrated, preventing dryness that can worsen symptoms18. For severe cases, topical corticosteroids are recommended, while oral corticosteroids may be prescribed for more extensive skin coverage18.
The American Contact Dermatitis Society’s Contact Allergen Management Program (CAMP) helps generate a “safe list” of products for patients19. This program is useful for creating a personalized plan for managing dermatitis. Avoiding common irritants and carefully selecting skin care products can significantly reduce the risk and frequency of allergic reactions.
A diet low in nickel and other minerals has been reported to improve symptoms of allergic contact dermatitis in some patients19. For accurate and detailed diagnosis and treatment options, more information can be explored on contact dermatitis causes and symptoms.
Allergic Eczema: Causes and Solutions
Allergic eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, occurs when the body reacts to allergens, causing itchy, inflamed skin patches. It often starts in young children, with symptoms appearing before age 5 and sometimes lasting into adulthood21. Those with a family history of asthma or hay fever and food allergies, like to eggs and cow’s milk, are more likely to be affected2221.

Understanding Allergic Eczema
Eczema is caused by a mix of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Common allergens include nickel, perfumes, certain fabrics, latex, and cleaning products23. Symptoms like itching, burning, and skin color changes can appear within hours to 10 days after exposure23. Identifying these triggers is key to managing the condition.
Best Treatments for Relief
Effective treatment begins with avoiding known allergens through patch testing23. Topical corticosteroid creams are commonly used to reduce inflammation and itching23. For severe cases, stronger medications or corticosteroid pills may be prescribed23. Keeping the skin hydrated with emollients and a regular moisturizing routine is also essential21.
Consistent proactive management of eczema can greatly improve quality of life. Recognizing triggers and following treatment plans can significantly help222123.
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease: Symptoms and Care
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) mainly hits young children, often those under 5 to 7 years24. It’s usually caused by coxsackievirus 16, a nonpolio enterovirus24. Symptoms show up 3 to 5 days post-infection25 and peak contagiousness is in the first week24. Keeping hands clean and practicing good hygiene can lower infection risks24.
Signs to Look For
Look out for mouth sores and a rash on hands and feet to spot HFMD. Other signs include fever, sore throat, and painful blisters24. Dehydration is common due to swallowing issues from mouth sores, sometimes needing IV fluids24. Rarely, HFMD can cause viral meningitis or encephalitis24.
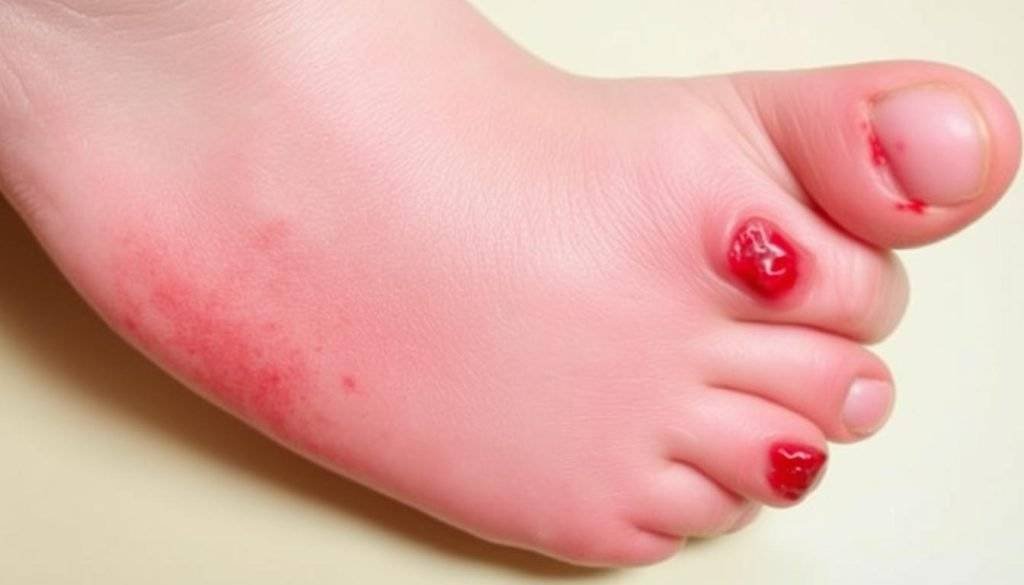
Treating Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Most people get better in 7 to 10 days without much treatment, but HFMD care aims to ease symptoms25. Here are some effective ways to treat HFMD:
- Mouth Rinses: Use mouth rinses to soothe sores.
- Fever Reducers: Use over-the-counter meds like acetaminophen or ibuprofen to lower fever and ease pain.
- Hydration: Make sure your child drinks lots of fluids to avoid dehydration.
Good hygiene is key to stopping the spread of this disease. Wash hands often, after diaper changes, and clean common areas well. This helps keep kids in childcare safe from infection24. By doing these things, you can help manage symptoms and quicken recovery, reducing the risk of complications from HFMD.
Diaper Rash: Prevention and Treatment
Diaper rash is a common issue in infants, causing red, inflamed skin on their bottom. It often results from prolonged exposure to wet or soiled diapers. Understanding the symptoms and implementing effective treatment methods are key to managing diaper rash.
Symptoms of Diaper Rash
Parents need to watch for diaper rash symptoms like redness, swelling, and tenderness in the diaper area. Babies with atopic dermatitis or other skin conditions are more likely to get diaper rash26. Antibiotics can also disrupt protective bacteria, raising the risk of rashes26. If a rash persists and doesn’t improve with basic treatments, a dermatologist visit may be needed to avoid complications like post-inflammatory hypopigmentation27.
Effective Treatment Methods
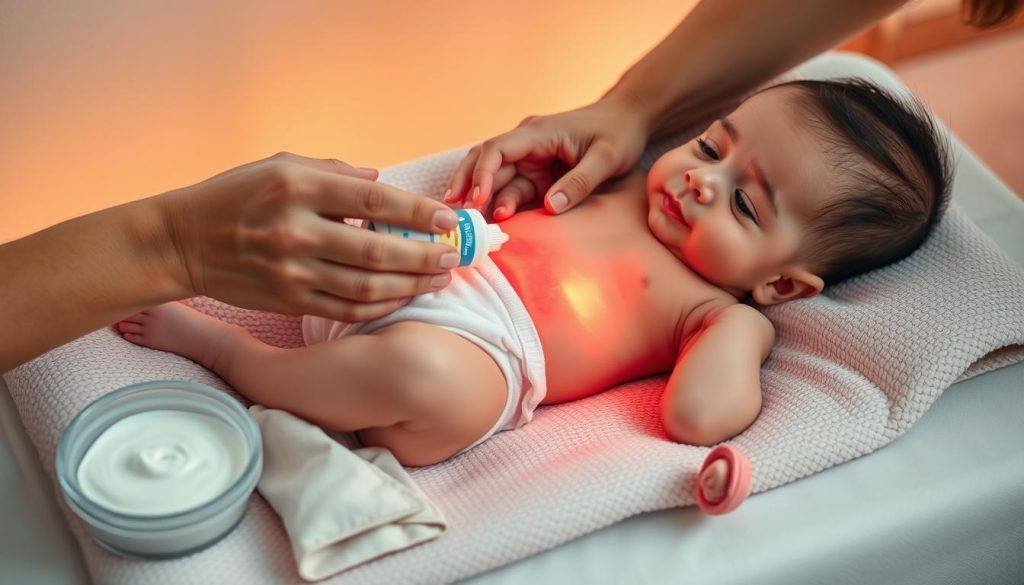
Effective treatment for diaper rash involves a multi-faceted approach:
- Change Diapers Frequently: Keeping the baby’s bottom clean and dry is essential. Wet or soiled diapers should be changed quickly to prevent irritation26.
- Use Barrier Creams: Applying creams with zinc oxide or petroleum jelly at each diaper change protects sensitive skin26. Over-the-counter options include A + D, Balmex, Desitin, and Triple Paste27.
- Maintain Airflow: Allowing the baby to go diaper-free for short periods helps the skin breathe and heal faster. Wearing looser-fitting diapers can also reduce irritation26.
- Topical Applications: For severe cases, antifungal creams should be applied twice daily if a fungal infection is present. Mild hydrocortisone creams can help with inflammation27.
- Daily Bathing: Use warm water and mild soap for bathing until the rash clears. Avoid products with harmful substances like baking soda, boric acid, camphor, phenol, benzocaine, diphenhydramine, or salicylates27.
Preventing diaper rash requires proactive infant skin care practices. Regular diaper changes, cleanliness, and gentle skin care products are essential. These steps can significantly reduce diaper rash symptoms, ensuring your baby’s comfort and well-being.
Eczema: Managing Flare-Ups
Understanding eczema’s triggers and using various treatments is key to managing flare-ups. This condition affects 10-20% of children and 1-3% of adults worldwide. It is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin patches28.

Identifying Common Triggers
Identifying eczema triggers is essential for managing flare-ups. About 50% of patients point to soaps and detergents as irritants. Stress is a trigger for 30-50% of patients28. Weather, like dry winter air, affects 75% of individuals28. Avoiding these triggers can greatly reduce flare-up frequency and severity.
Top Treatment Approaches
Treating eczema requires a multi-faceted approach. Moisturizing regularly is a fundamental part of skin care routines for eczema. Topical corticosteroids offer relief in about 80% of cases when used correctly28. Phototherapy improves symptoms in about 60% of patients, while dupilumab (Dupixent) has shown a 38% symptom reduction in trials2829.
Daily baths or showers in warm water for less than 10 minutes are beneficial. Applying moisturizer within three minutes after drying is essential29. Nonprescription creams with at least 1% hydrocortisone provide temporary itching relief when used no more than twice a day29.
For severe cases, wet dressings and bleach baths are recommended29. Stress management and mental health care are also critical. Stress and emotional disorders can worsen atopic dermatitis symptoms29.
For more detailed information on managing eczema flare-ups, visit the Eczema Flare-ups Guide.
Psoriasis: Chronic Skin Condition
Psoriasis is a prevalent chronic skin condition, impacting 2-3% of the world’s population3031. It causes skin cells to rapidly multiply, resulting in thick, scaly plaques. In psoriasis sufferers, skin cell turnover is significantly accelerated, occurring in just 3-4 days, as opposed to the normal 28-30 days30.
What Triggers Psoriasis?
Several factors can trigger psoriasis flare-ups, making it challenging to manage. Emotional stress is a major trigger, affecting 60-70% of those with psoriasis30. Infections, like streptococcal infections, also trigger flare-ups in 10-20% of cases30. Other common triggers include skin injuries, certain medications, smoking, and heavy alcohol consumption31. It’s important to note that psoriasis is not contagious and cannot be spread through skin contact or shared items3031.
Treatment Options Available
Various treatments exist for psoriasis, depending on its severity and type. Mild cases often respond well to topical treatments like corticosteroids and vitamin D analogues. Phototherapy, which involves ultraviolet light exposure, is also effective. For more severe cases, systemic drugs like biologics can be prescribed to control the immune system. These treatments aim to reduce inflammation, slow cell turnover, and clear plaques, providing significant relief.
Lifestyle Changes for Relief
A suitable lifestyle is essential for managing psoriasis effectively. Stress management through meditation and yoga can help alleviate flare-ups. A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, combined with regular exercise, promotes health and reduces symptoms. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption also helps manage symptoms. These lifestyle adjustments can prevent comorbid conditions like high blood pressure and type 2 diabetes, which psoriasis patients are at higher risk for31.
For more detailed information on psoriasis triggers and treatments, you can visit this resource that offers additional insights into managing and understanding chronic skin conditions.
Chickenpox: Identifying and Managing This Viral Rash
Chickenpox is a common viral rash characterized by an itchy, blister-like rash that spreads across the body. It usually lasts between 4 to 7 days32 Children often miss 5 to 6 school or childcare days due to this infection32. High-risk groups include infants, adolescents, pregnant women, and those with weakened immune systems. This includes individuals with HIV/AIDS, cancer patients, transplant recipients, and those on immunosuppressive medications32.
Identifying chickenpox is often straightforward based on the observable rash according to the Mayo Clinic33. Blood tests or studies of affected skin can confirm the diagnosis if needed33. In healthy children, chickenpox usually requires no specific medical treatment and will resolve on its own. Antihistamines can help with itching, while antiviral medications like acyclovir are most effective within 24 hours of the rash’s appearance to reduce severity33. It’s important to remember that chickenpox is highly contagious until all blisters have fully crusted over33.
The introduction of the varicella vaccine in 1995 significantly diminished the prevalence of chickenpox. It recommends two doses for children, teens, and nonimmune adults as stated by Well Natural Health34. Despite vaccination efforts, some vaccinated individuals might contract chickenpox. Their symptoms are typically milder and accompanied by fewer or no blisters32. Vaccination post-exposure can help prevent the disease or lessen its severity33.
In terms of chickenpox management, itch relief is key for comfort. Calamine lotion and oatmeal baths provide soothing effects. For fever, pain relievers like acetaminophen are advised. It is strongly recommended to avoid giving aspirin to children or teenagers with chickenpox due to the risk of Reye’s syndrome33. In cases of serious complications, such as secondary bacterial infections or pneumonia, antibiotics and antiviral medications like acyclovir are necessary. Continuous monitoring of symptoms like high fever, which lasts beyond four days or exceeds 102°F (38.9°C), requires immediate professional medical attention33.
Lupus Rash: Autoimmune Skin Issues
Understanding and recognizing lupus symptoms is vital for effective lupus management. A key symptom is the presence of skin rashes, often seen as a butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and nose, known as the “malar rash.” This rash is a hallmark of systemic lupus, affecting about 30% of patients35. It’s also more common in people of color, with rashes appearing dark purple or dark brown, unlike the typical red or pink hues35.
Symptoms and Appearance
Lupus rashes can take many forms, including hives, angioedema, and skin ulcers, common in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients35. Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) is the most common form of cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE). It can cause temporary or permanent hair loss when lesions occur on the scalp36. Chronic discoid lupus rashes may also increase the risk of developing skin cancer, such as squamous cell carcinoma, in lesions on the lips or inside the mouth36.
Managing Lupus-Related Skin Issues
Treating lupus rash requires a holistic approach. It’s important to avoid triggers like sun exposure and certain medications. Acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (ACLE) rashes can appear flat, raised, or scaly and may itch, though they are generally not painful36. Around 20% of individuals first diagnosed with CLE will progress to SLE, highlighting the need for vigilant lupus management36. Treatments include topical corticosteroids, sun protection, and systemic medications for severe cases.
Combining medical treatments with lifestyle modifications can greatly improve life quality for those managing autoimmune skin conditions. For example, the Lupus Foundation is working to increase awareness and representation of lupus symptoms in diverse skin tones, leading to better diagnosis and treatment strategies35. A proactive and informed approach is essential for treating lupus rash and addressing the broader spectrum of lupus symptoms.
Shingles: Reactivated Chickenpox Virus
Shingles is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus that leads to chickenpox. It often presents as a painful rash and can cause severe complications, mainly in older adults. People over 50 are more likely to get shingles, with the risk increasing with age and past chickenpox infections37.
Symptoms of Shingles
The shingles symptoms start with tingling or pain on one side of the body, followed by a rash. Within 24 hours, the rash turns into fluid-filled blisters, causing significant discomfort38. Shingles near the eyes can lead to vision loss, causing painful ocular infections37.
Treatment Options
Antiviral medications can help manage shingles, reducing the risk of long-term pain like postherpetic neuralgia, affecting 10% to 18% of patients37. Shingrix, a vaccine for adults 50 and older, offers over five years of protection against shingles37. It’s important to manage side effects like redness and swelling to ensure the vaccine’s benefits outweigh its minor drawbacks.
Preventing Shingles
Vaccination is key in preventing shingles. The CDC recommends Shingrix for all adults 50 and older38. A healthy lifestyle, including stress management and adequate sleep, may also help prevent shingles, though no direct correlation with sleep duration has been found39. The live shingles vaccine (Zostavax) is no longer available in the U.S., making Shingrix the preferred option for prevention37.
A study found a 72% lower shingles incidence in children vaccinated against chickenpox39. This highlights the long-term benefits of early immunization. Viral infections like RSV and COVID-19 can worsen respiratory symptoms, stressing the need for early medical intervention39.
Vaccine efficacy can wane over time, requiring booster shots for continued protection39. It’s essential to stay current with vaccinations and maintain vigilant health practices to reduce shingles prevalence and impact.
Conclusion
Understanding rashes is essential for effective management and skin health. This guide has provided you with the knowledge to tackle common skin issues. From identifying causes to recognizing symptoms and choosing treatments, you’re now equipped.
Skin rashes stem from infections, allergies, and environmental factors. Conditions like eczema and psoriasis often have a genetic link, making rash management and preventive skincare critical40. Allergic reactions, such as contact dermatitis and hives, require specific treatments41. Bacterial and fungal infections highlight the importance of hygiene and timely medical advice.
To maintain skin health, avoid irritants and use hypoallergenic products. Good hygiene practices are also key. For minor symptoms, over-the-counter treatments and cool compresses can help. But, for severe or persistent rashes, seeking healthcare advice is vital for proper care42. Stay informed about skin conditions and take proactive steps in your skincare routine for healthier skin. Always consult professionals for issues beyond routine care to protect your skin’s health.
FAQ
What is a skin rash?
A skin rash is an area of inflamed or discolored skin, often accompanied by itching, pain, or dryness. It can be caused by allergies, irritants, microbial infections, or systemic diseases.
What are common causes of skin rashes?
Common causes include infections, autoimmune disorders, environmental factors, and allergic reactions. Identifying the specific cause is essential for effective treatment.
What are the symptoms to watch for in skin rashes?
Symptoms often include redness, blisters, peeling skin, itching, and severe discomfort. Accurate identification of these symptoms is critical for proper management.
How do flea bites appear and what are their symptoms?
Flea bites appear as small, itchy clusters or lines on the lower legs and feet, becoming red and swollen. Symptoms often worsen at night.
What steps should be taken for effective treatment of flea bites?
Treatment includes thorough cleaning of the affected area and applying topical antihistamines or corticosteroids to reduce itching and inflammation.
How can you recognize fifth disease in children?
Fifth disease is characterized by a distinctive “slapped cheek” appearance followed by a spreading body rash, mild fever, and fatigue.
What are the treatment options for fifth disease?
Treatment focuses on symptom relief, such as fever reducers and adequate hydration. Ensuring good hygiene practices can help prevent the spread.
What are some triggers of rosacea?
Triggers include hot drinks, spicy foods, temperature extremes, and stress. Identifying personal triggers is key to managing the condition.
What treatments are effective for rosacea?
Treatments often involve topical and oral medications to reduce inflammation and redness, laser therapy for severe cases, and a tailored skincare regimen.
What are the symptoms and causes of impetigo?
Impetigo symptoms include red sores that quickly rupture to form honey-colored crusts, mainly around the nose and mouth, caused by streptococcus or staphylococcus bacteria.
How should impetigo be treated?
Treatment involves antibiotic creams and, in severe cases, oral antibiotics. Proper hygiene and isolating affected individuals until non-contagious helps prevent spread.
How can you identify ringworm?
Ringworm presents as circular, red, scaly patches with a clearer center, spreading through skin-to-skin contact or shared items like towels.
What are the treatment and medication options for ringworm?
Treatment typically involves antifungal creams or oral medication for widespread infections. Maintaining skin hygiene helps prevent the spread.
How can the spread of ringworm be prevented?
Preventive measures include maintaining skin hygiene and avoiding shared personal items.
What are the causes of contact dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis results from skin contact with allergens or irritants like plant sap, metals, and cosmetic products.
What are common symptoms and how is contact dermatitis diagnosed?
Symptoms include red, itchy, and inflamed skin. Diagnosis often involves patch testing to identify specific allergens.
What treatment options are available for contact dermatitis?
Treatment involves corticosteroid creams, oral antihistamines, and avoiding known irritants.
What is allergic eczema?
Allergic eczema occurs when allergens such as perfume, animal dander, and certain fabrics contact the skin, leading to itchy and inflamed patches.
What are the best treatments for allergic eczema?
Identifying triggers through patch testing, using topical steroids to manage flare-ups, and maintaining skin moisture through emollients are effective treatments.
What are the signs to look for in hand, foot, and mouth disease?
Symptoms include sores in the mouth, rash on the hands and feet, fever, sore throat, and painful blisters.
How can you treat hand, foot, and mouth disease?
Treatment focuses on symptom relief, such as mouth rinses for soreness and fever reducers. Good hygiene practices can help prevent the disease from spreading.
What are the symptoms of diaper rash?
Symptoms of diaper rash include red and inflamed skin on a baby’s bottom, often caused by prolonged exposure to a wet diaper.
What are effective treatment methods for diaper rash?
Treatment includes frequent diaper changes, air drying, and using barrier creams to protect sensitive skin. Keeping the baby’s bottom clean and dry helps prevent the rash.
What are common triggers for eczema?
Triggers include soaps, detergents, stress, and weather changes. Understanding these triggers helps in managing flare-ups.
What are the top treatment approaches for eczema?
Managing eczema involves regular moisturizing, using medicated creams like corticosteroids, and avoiding triggers. Advanced cases might need phototherapy or systemic medications.
What triggers psoriasis?
Psoriasis can be triggered by factors such as stress, skin injury, and certain medications. Recognizing and managing triggers can help alleviate symptoms.
What treatment options are available for psoriasis?
Treatment options include topical treatments, phototherapy, and systemic drugs. Lifestyle adjustments like stress management and a balanced diet can also ease symptoms.
What are some lifestyle changes for relief from psoriasis?
Stress management, a balanced diet, and avoiding known triggers are important lifestyle changes that can alleviate psoriasis symptoms.
How can you identify and manage chickenpox?
Chickenpox is characterized by an itchy, blister-like rash, often accompanied by fever and tiredness. Management includes itch relief, pain relievers for fever, and vaccination for prevention.
What are the symptoms and appearance of a lupus rash?
Lupus can cause a distinct butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and nose, often worsening with sun exposure.
How can you manage lupus-related skin issues?
Management includes topical treatments, sun protection, and systemic medications for severe cases. Recognizing and avoiding triggers is critical.
What are the symptoms of shingles?
Shingles causes a painful rash, usually appearing as a band on one side of the body, resulting from the reactivation of the chickenpox virus.
What are the treatment options for shingles?
Early treatment with antiviral medication can reduce the severity and prevent long-term pain. Vaccination is recommended for older adults to lower the risk of shingles.
How can you prevent shingles?
Vaccination is the most effective method to reduce the risk of shingles, specially recommended for older adults.
Source Links
- https://www.healthline.com/health/rashes – 22 Common Skin Rashes: Pictures, Causes, and Treatment
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/rash-pictures-4020312 – How to Identify 10 Common Skin Rashes
- https://www.health.com/skin-rash-7372022 – How To Identify Different Kinds of Skin Rashes
- https://www.uchealth.org/diseases-conditions/skin-rashes/ – Skin rashes
- https://medlineplus.gov/rashes.html – Rash | Dermatitis | Skin Rash | MedlinePlus
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/311941 – Fleabites: Symptoms, causes, risks, and treatment
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK541118/ – Flea Bites – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21718-flea-bites – Flea Bites: What They Look Like, Symptoms & Treatment
- https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/fifth.html – Fifth Disease (for Parents)
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15774-fifth-disease – Fifth Disease
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/rosacea/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353820 – Rosacea – Diagnosis and treatment
- https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/rosacea – Rosacea
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/impetigo/ – Impetigo
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/impetigo/symptoms-causes/syc-20352352 – Impetigo-Impetigo – Symptoms & causes – Mayo Clinic
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15134-impetigo – Impetigo, Contagious Skin Infection: Causes, Treatment & Prevention
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ringworm-body/symptoms-causes/syc-20353780 – Ringworm (body): How to treat this skin infection-Ringworm (body) – Symptoms & causes – Mayo Clinic
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4560-ringworm – Ringworm (Tinea Corporis): What It Looks Like, Causes & Treatment
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/contact-dermatitis/ – Contact dermatitis
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532866/ – Allergic Contact Dermatitis – StatPearls
- https://dermnetnz.org/topics/allergic-contact-dermatitis – Allergic Contact Dermatitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment – DermNet
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/atopic-dermatitis-eczema/symptoms-causes/syc-20353273 – Atopic dermatitis (eczema) – Symptoms and causes
- https://acaai.org/allergies/allergic-conditions/skin-allergy/eczema/ – Eczema | Causes, Symptoms & Treatment | ACAAI Public Website
- https://www.healthline.com/health/skin/eczema – Allergic Eczema: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hand-foot-and-mouth-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20353035 – Hand-foot-and-mouth disease-Hand-foot-and-mouth disease – Symptoms & causes – Mayo Clinic
- https://www.cdc.gov/hand-foot-mouth/signs-symptoms/index.html – HFMD Symptoms and Complications
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diaper-rash/symptoms-causes/syc-20371636 – Diaper rash: Home treatments usually work-Diaper rash – Symptoms & causes – Mayo Clinic
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diaper-rash/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20371641 – Diaper rash: Home treatments usually work-Diaper rash – Diagnosis & treatment – Mayo Clinic
- https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/eczema/live-better-eczema – Get Your Eczema Under Control: Top Triggers and Prevention Tips
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/atopic-dermatitis-eczema/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353279 – Atopic dermatitis (eczema) – Diagnosis and treatment
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/6866-psoriasis – Psoriasis: What It Is, Symptoms, Causes, Types & Treatment
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/psoriasis/symptoms-causes/syc-20355840 – Psoriasis – Symptoms and causes
- https://www.cdc.gov/chickenpox/signs-symptoms/index.html – Chickenpox Symptoms and Complications
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/chickenpox/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20351287 – Chickenpox – Diagnosis and treatment
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/chickenpox – Chickenpox
- https://www.lupus.org/resources/lupus-and-skin-rashes – Lupus and Skin Rashes
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/23163-lupus-rash – Lupus Rash: Types, Causes, Treatment & Prevention
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/shingles/symptoms-causes/syc-20353054 – Shingles-Shingles – Symptoms & causes – Mayo Clinic
- https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/report/shingles-and-chickenpox-varicella-zoster-virus – Shingles and chickenpox (Varicella-zoster virus) Information | Mount Sinai
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/11036-shingles – Shingles (Herpes Zoster): Symptoms & Treatment
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2515356/ – Allergy and the skin – PMC
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/317999 – Skin rash: Causes, 71 pictures of symptoms, and treatments
- https://www.sprintdiagnostics.in/blog/skin-rashes-causes-types-and-care – Skin Rashes: Causes, Types, and Care | Sprint Diagnostics












